JAVAJEE.COM
Engineering Full Stack Apps with Java and JavaScript
Introduction to Spring MVC
The Spring MVC framework provides model-view-controller architecture and also provides many components that can be used to develop web applications.
Model-view-controller (MVC)
-
Model-view-controller (MVC) is a software architectural pattern for implementing web applications with user interfaces.
-
MVC decouples business logic from UIs.
-
MVC divides a given software application into three interconnected parts called Model, View and Controller, so as to separate internal representations of information from the ways that information is presented to or accepted from the user.
-
MVC design defines the interactions between Model, View and Controller as:
-
Controller
-
receives requests from users
-
send commands to the model to update the model's state.
-
send commands to its associated view to change the view's presentation of the model.
-
-
Model
-
encapsulates and stores application data that will be shown in the UI
-
data stored in model is retrieved according to commands from the controller and displayed in the view.
-
-
View
-
generates an output presentation to the user based on changes in the model.
-
should not have any business logic.
-
-
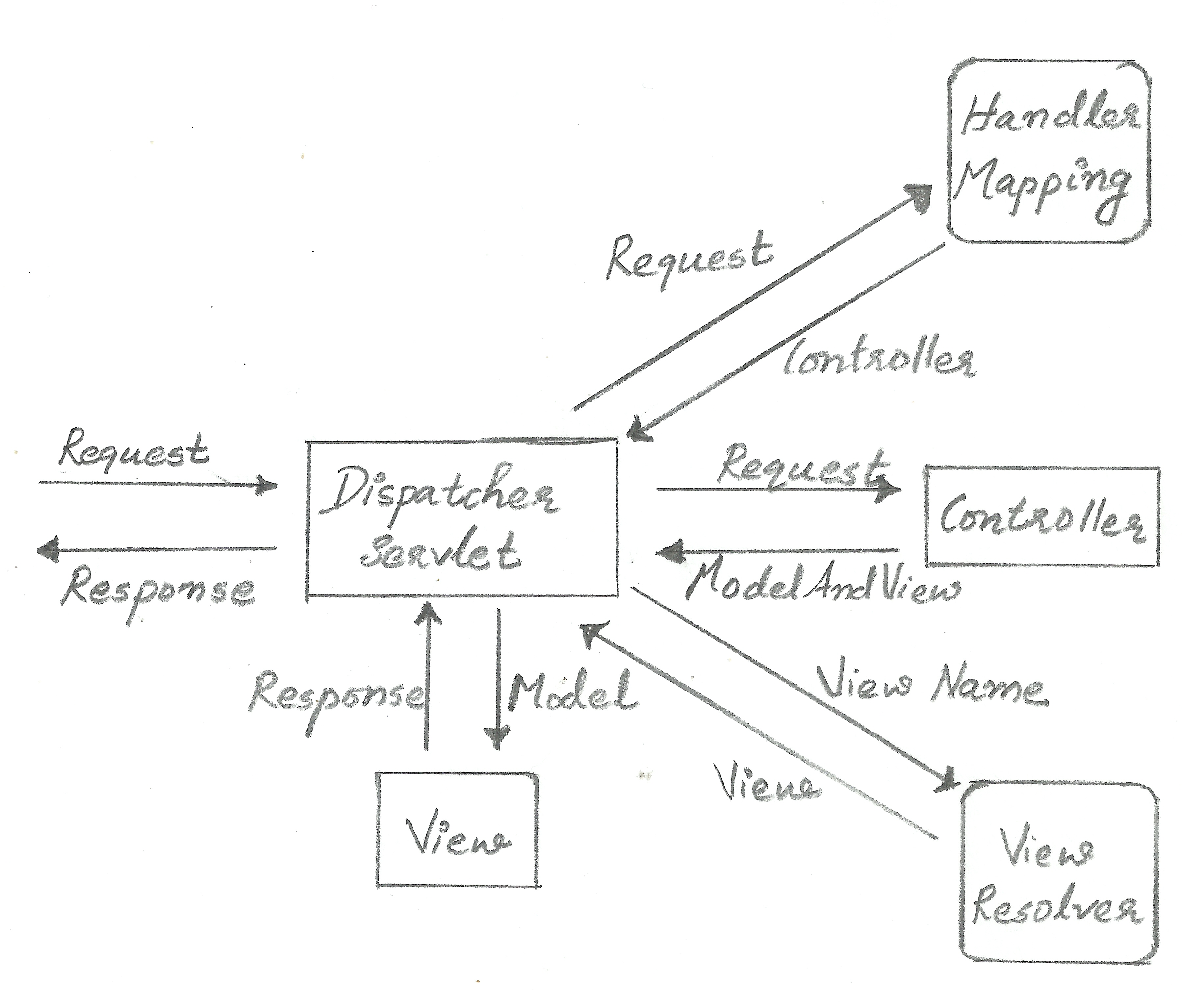
Overview of Spring MVC Request Handling
-
In Spring MVC, models usually consist of domain objects.
-
These domain objects are processed by the service layer and persisted by the persistence layer.
-
-
Views can be a JSP template written with Java Standard Tag Library (JSTL) or even PDF files, Excel files, RESTful web services or a Rich Internet Application (RIA) framework such as Adobe Flex.
-
One of the application I had worked with had Spring, Adobe Flex and Hibernate, used together.
-
-
Controller is the most important component and is usually configured in the application deployment descriptor web.xml or through annotations.
-
The controller implements the front controller design pattern and often called as Dispatcher Servlet.
-
Every web request must go through the controller.
-
A controller map requests to a handler method by one or more handler mappings.
-
When a controller receives a request, it uses the handler mappings to find the right handler method.
-
-
After a handler method processes the request, it return a logical view name.
-
If the return type of the handler method is void, a default logical view name based on a handler method’s or controller’s name may be used.
-
-
A view resolver resolves a logical view name into a specific view implementation.
-
The view implementation renders the objects passed by controller's handler method.
-
-
Spring MVC general request handling diagram
- heartin's blog
- Log in or register to post comments
